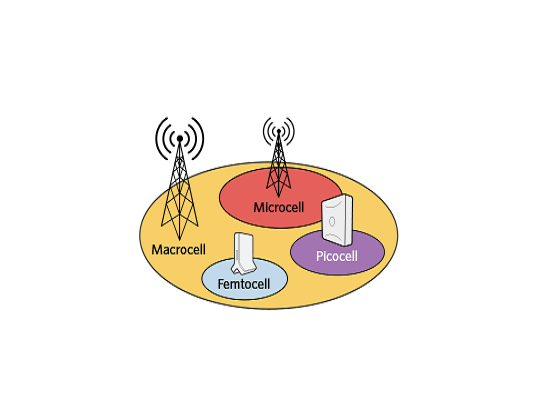
Heterogeneous Networks using Small Cells
As a consequence of the proliferation of smart phones and tablets, data traffic is growing significantly, both on the radio access links and the backhaul infrastructure of mobile operators’ networks. And although LTE and LTE Advanced offer higher data traffic throughput than that of 3G, given to their wider allocated bandwidths, the combined capacities of even these networks is not sufficient to meet projected future capacity demands. The conventional solution to increasing the capacity of LTE mobile networks includes splitting macro-cells and/or adding more sites. Both of these solutions require high CAPEX and OPEX, so mobile operators are seeking new and cost effective ways of increasing their network capacity. One solution is to deploy small-cell base stations (BSs) within their existing macro-cellular networks, an approach referred to as Heterogeneous Networks.
A Heterogeneous Network (HetNet) consists of two levels of BS: Macro-Cellular BSs (MCBSs) and underlying Small-Cell BSs (SCBSs); these can use the same technology (e.g. LTE) or different technologies (LTE and WiFi). It is well known that a HetNet not only increases the network capacity, but also provides better coverage and enhances the user’s experience.
